Increasing crop yields is based on improving plant nutrition and soil health.
Aug. 1, 2025, 2:19 p.m.
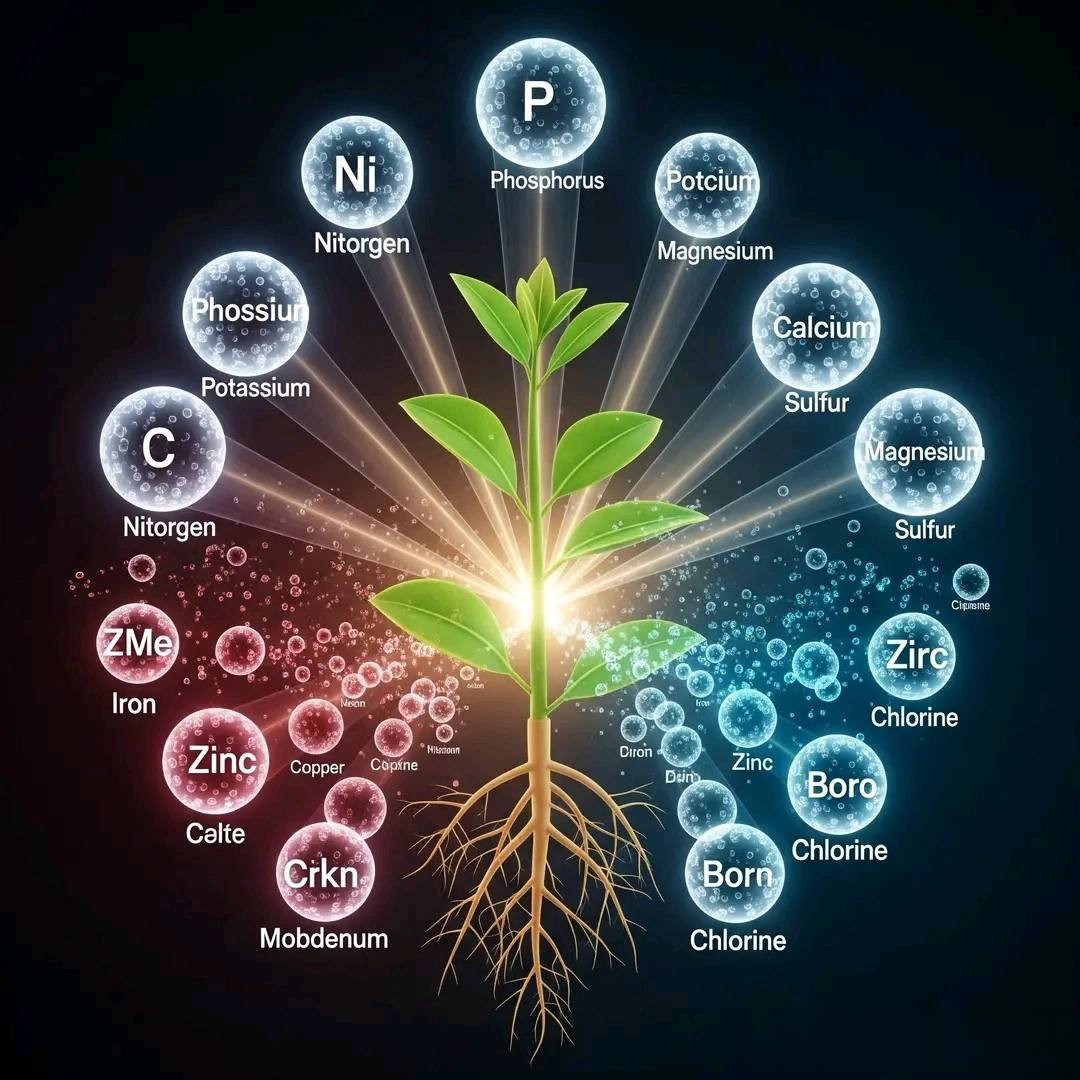
Macronutrients.
Macronutrients are elements that plants need in relatively large quantities. They are the main component in the physical formation of plants and are important for the growth of organic substances.
Different macronutrients and their functions:
* Nitrogen (N): plays a vital role in the formation of plant cells, tissues, and organs (roots, stems, leaves, and also at the beginning of flower formation). Nitrogen is the main ingredient of chlorophyll, protein, and amino acids, so it is essential for vegetative growth.
* Phosphorus (P): necessary for vegetative growth, such as root formation, cell nucleus and cell division. Phosphorus also stimulates flowering, seed formation and enhances plant resistance to disease.
* Potassium (K): serves as a regulator of plant physiological processes such as photosynthesis, accumulation, translocation, and transport of carbohydrates. Potassium also helps regulate water distribution in tissues and cells and increases plant resistance to pests and diseases.
* Calcium (Ca): It plays a role in the formation and processing of cell walls, making it an intercellular adhesive substance. Calcium is also important for root system growth and optimization of nitrogen absorption.
* Magnesium (Mg): It is the main component of chlorophyll (the green substance in leaves), so it is essential for the smooth process of photosynthesis. Magnesium also plays a role in nitrogen and carbohydrate metabolism.
* Sulfur (S): plays a role in the formation of proteins (especially the amino acids cysteine and methionine) and vitamins. Sulfur also helps stimulate the formation of root nodules in legumes and facilitates the work of other nutrients.
Trace elements:
Trace elements are elements that plants need in smaller quantities than macronutrients. However, trace elements play a very important and decisive role in maintaining various biochemical and metabolic processes in plants. A deficiency or excess of trace elements can cause serious plant growth disorders.
Different trace elements and their functions:
*Iron (Fe): Important for the formation of chlorophyll, enzymes, protein components, and plays a role in chloroplast development and protein synthesis.
*Manganese (Mn): Serves as an activator of various enzymes involved in the assimilation and synthesis of proteins and carbohydrates.
* Copper (Cu): Serves as a building block for enzymes and participates in the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates. Copper also supports electron transport in photosynthesis.
* Zinc (Zn): Important for the formation of the natural growth hormone (auxin) and activates enzymes that form proteins and carbohydrates.
* Boron (B): Plays a role in the transport of sugars in the plant body, supporting potassium and calcium metabolism, and is important for the formation of shoot cells, pollen, flowers, and roots.
* Molybdenum (Mo): Serves to activate the enzyme nitrogenase (which plays a role in binding nitrogen from the air by root nodule bacteria on legumes) and nitrate reductase.
* Chlorine (Cl): Increases cell osmotic pressure, regulates respiration, and plays a role in photosystem II in the process of photosynthesis (especially in the evolution of oxygen).
Key difference between macro- and micronutrients.
The fundamental difference between macro- and micronutrients lies in the amount required by plants.
Macronutrients are needed in large quantities (total concentration > 1000 mg/kg dry matter), while micronutrients are needed in very small quantities (total concentration < 100 mg/kg dry matter). However, both macro- and micronutrients are essential for healthy plant growth and development.
It should be noted that modern agronomy is not just a mathematical calculation of the nutrients and compounds necessary for a good harvest.
Leading agricultural companies strive to accurately analyze and predict the application of fertilizers and plant protection products. Modern standards of agricultural product control stimulate the development of organic farming and the use of nature-based solutions.
Smart Solution TM's work is aimed at introducing innovative developments for soil remediation and improving fertilizer absorption. The environmental results of our efforts are a total reduction in the use and, therefore, accumulation of mineral fertilizers in the soil, improvement of microbiological parameters, and an overall reduction in the impact of climatic factors.
Aug. 1, 2025, 2:19 p.m.